- #11-13 Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre (Orchard)
- Mon Fri 9am — 6pm | Sat 9am — 12.30 pm
Achilles tendinopathy (Heel pain) is an overuse injury that involves inflammation or degeneration of the Achilles tendon. It is often caused by repetitive strain from activities such as running, jumping, or sudden changes in intensity during exercise.
Heel pain can make your daily activities difficult. A common culprit of this discomfort is Achilles tendinopathy, also known as Achilles tendonitis. The condition affects the Achilles tendon, the largest tendon in the body, which connects the calf muscle to the heel bone.
Several factors can contribute to Achilles tendinopathy:
Achilles tendinopathy usually presents with the following symptoms:
A specific form of Achilles tendinopathy is insertional Achilles tendinopathy, which affects the area where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. This type of tendinopathy is often accompanied by pain and tenderness near the bottom of the heel, especially during activities that involve pushing, such as running uphill or climbing stairs.
Although the activities and mechanics described above directly contribute to the development of Achilles tendinopathy, certain factors make people more susceptible to experiencing the condition:
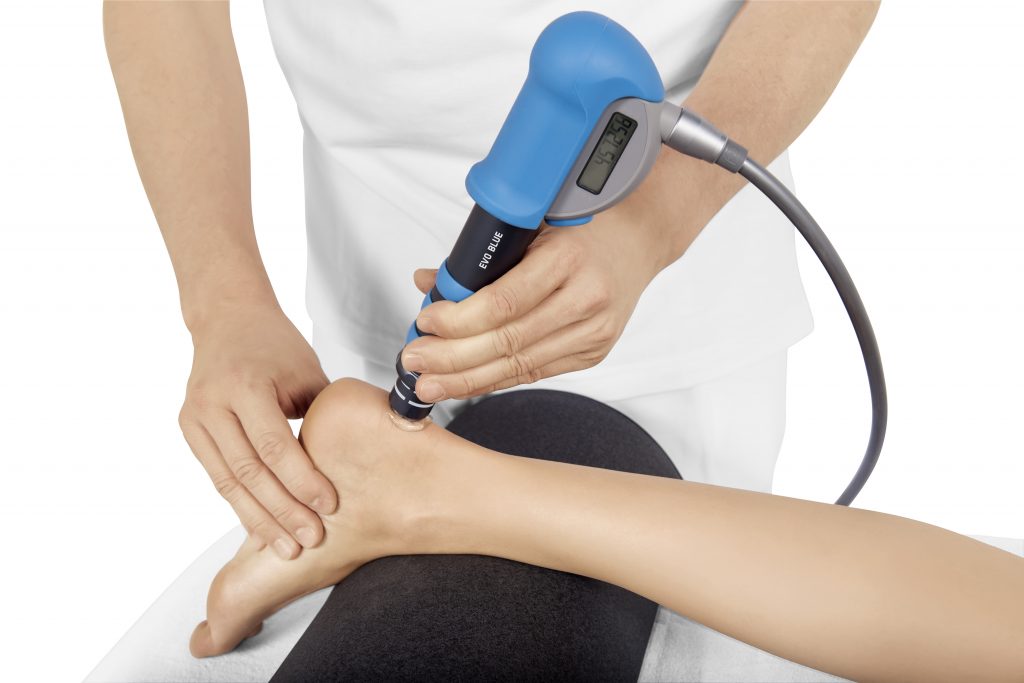
If you suspect Achilles tendinopathy, consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. They will likely perform a physical exam, ask about your medical history and activity level, and may recommend imaging tests such as x-rays or ultrasounds for further evaluation.
Fortunately, Achilles tendinopathy is usually treated with conservative measures:
In severe cases, where non-surgical approaches fail to provide adequate relief, your doctor might consider:
Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee Pain
Ankle Pain
Foot Pain
Book a consultation with us for a more comprehensive diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan best suited to your needs.

Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee
Ankle
Foot