- #11-13 Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre (Orchard)
- Mon Fri 9am — 6pm | Sat 9am — 12.30 pm
The hamstring muscles are powerful muscles responsible for hip flexion and knee extension. They are important for a variety of activities, including running, jumping, and kicking. Hamstring tendons connect these muscles to bones, transmitting the force generated by the muscles during movement.
Hamstring tendinopathy, sometimes called hamstring tendonitis, is a common condition that affects the tendon at the back of the thigh. These tendons connect the hamstring muscles (biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus) to the bones of the pelvis and lower leg. Hamstring tendinopathy involves inflammation, degeneration, or microtears in the hamstring tendon, often due to overuse or repetitive stress. This can cause pain, stiffness and weakness in the hamstrings, which can affect activities such as running, jumping and stair climbing.
Hamstring tendinopathy usually develops from overuse or repetitive strain on the hamstring tendon. This can be from:
The most common symptom of hamstring tendinopathy is pain in the back of the thigh, which can be:
Other possible symptoms may include:
It is important to remember that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
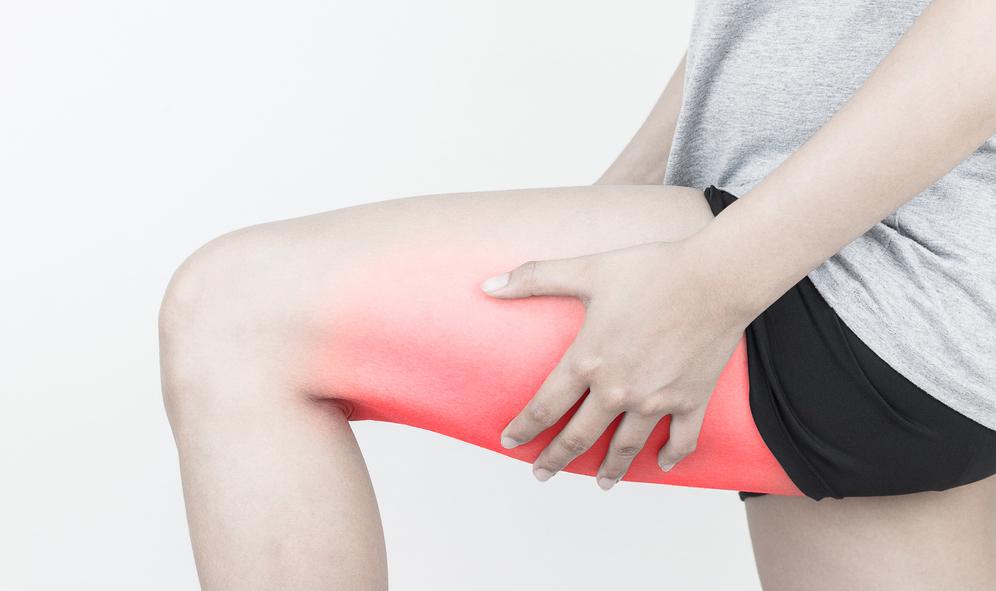
Although anyone can develop hamstring tendinopathy, certain factors can increase the risk:
A detailed discussion of your symptoms, activities, and any previous injuries with doctor is important to understand the context of your condition.
A detailed discussion of your symptoms, activities, and any previous injuries with doctor is important to understand the context of your condition.
A health care professional will examine the affected area for pain and tenderness. They will massage the hamstring muscles and tendons to pinpoint areas of pain and tenderness. They’ll assess your ability to bend forward, touch your toes, and fully extend your knee to assess flexibility and range of motion in the hamstrings.
Although not always necessary, imaging tests can sometimes be helpful in confirming a diagnosis and ruling out other possible causes of your pain. These may include:
Based on the medical history, physical examination, and results of any imaging tests, a healthcare professional will be able to diagnose hamstring tendinopathy and recommend the most appropriate treatment regimen.
Treatment usually involves a non-surgical approach, including:
In severe cases or if conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, other options may be considered, such as:
Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee Pain
Ankle Pain
Foot Pain
Book a consultation with us for a more comprehensive diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan best suited to your needs.

Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee
Ankle
Foot