- #11-13 Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre (Orchard)
- Mon Fri 9am — 6pm | Sat 9am — 12.30 pm
This page provides a clear overview of tennis elbow, its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options in Singapore, helping patients understand when specialist care may be required. At Auspicium Orthopaedic, patients are cared for by a neck and shoulder specialist with experience in managing upper limb and elbow-related conditions.
Spine
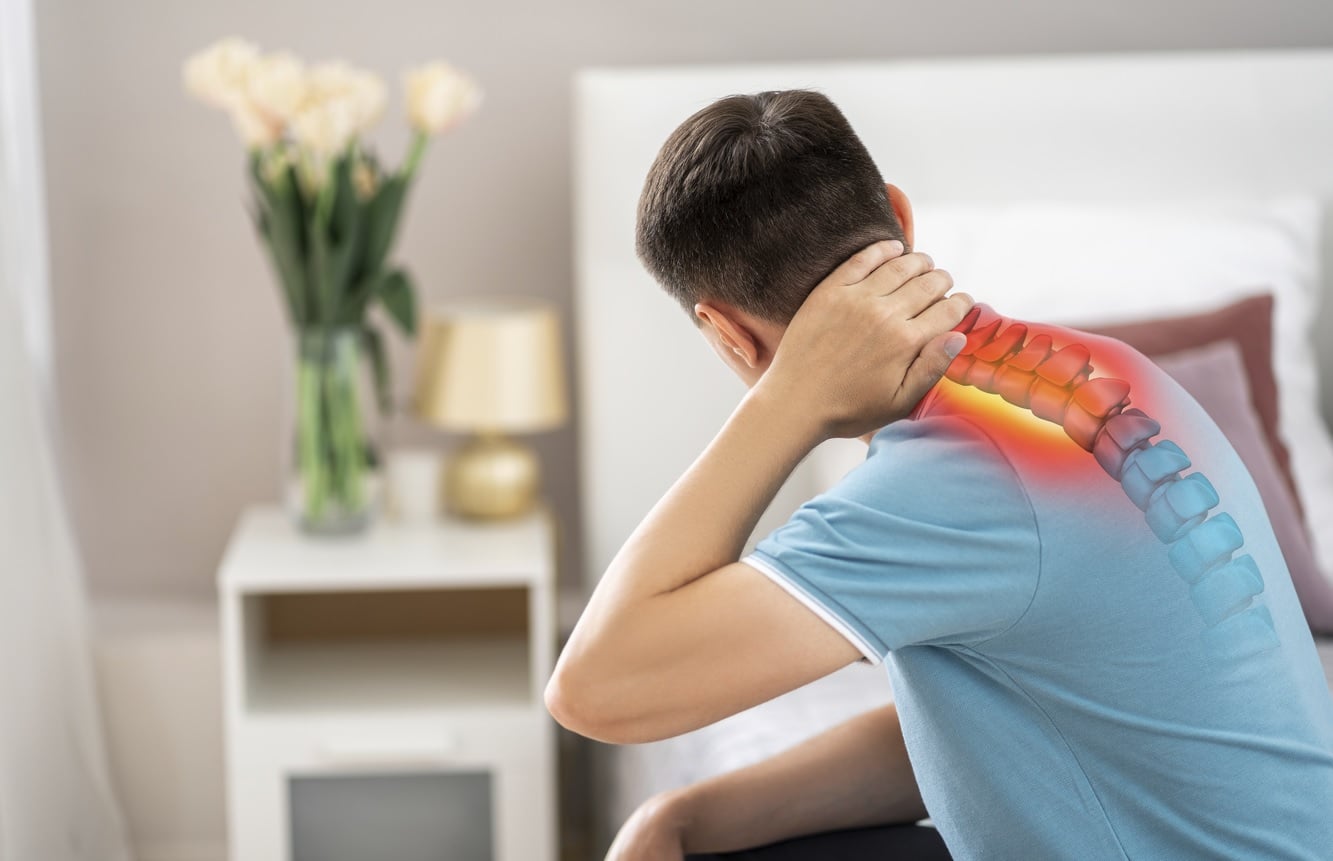
Facet arthropathy is a form of spine arthritis that affects the facet joints, which are small stabilising joints located at the back of the spine. When these joints undergo age-related wear and tear or degenerative changes, they can become inflamed, leading to back or neck pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
In the cervical spine, this condition is also referred to as cervical facet arthropathy or cervical facet osteoarthritis. The facet joints help guide and limit spinal movement, so degeneration may result in pain during neck rotation, extension, or prolonged postures. Symptoms can vary in severity and are often influenced by activity level, posture, and the extent of joint degeneration.
Several factors can contribute to the development of facet joint arthropathy of the neck:

The cervical spine is made up of seven vertebrae (C1-C7), each connected by facet joints at the back. These joints have a cartilaginous lining that provides smooth sliding surfaces and synovial fluid for lubrication. Additionally, ligaments and muscles surround the facet joints, providing stability and supporting movement. Facet joint arthropathy disrupts the normal structure and function of these joints. This may involve:
Several factors can contribute to the development of facet joint arthropathy of the neck:
Although anyone can develop cervical facet arthropathy, certain factors can increase the risk:
For facet arthropathy, the diagnosis involves assessing the patient’s medical history, conducting a physical examination, and considering imaging tests (such as X-rays) to evaluate the condition of the facet joints in the spine. The hallmark symptom is neck or back pain, which can worsen with certain movements.
Treatment for facet joint arthropathy in the neck typically involves a conservative approach to manage pain and improve function. This might include:
In some cases, if conservative approaches fail to provide adequate pain relief, minimally invasive procedures might be considered:
Facet joint replacement surgery is typically a last resort for individuals with severe and persistent pain who have exhausted all other conservative and minimally invasive options. This surgery involves replacing the damaged facet joint with an artificial implant.
The recovery time for facet joint arthropathy varies depending on the severity of the condition, treatment approach, and individual factors like adherence to treatment and overall health.
Typically, improvement with conservative measures like physical therapy and lifestyle modifications might be seen within weeks or months.
Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee Pain
Ankle Pain
Foot Pain
Book a consultation with us for a more comprehensive diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan best suited to your needs.

Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee
Ankle
Foot
You should consider seeing a neck and shoulder specialist if pain, stiffness, or weakness in the neck or shoulder persists for more than a few weeks, worsens over time, or affects daily activities such as work, sleep, or driving.
A neck and shoulder specialist manages a wide range of conditions, including cervical spine arthritis, facet joint arthropathy, disc-related neck pain, rotator cuff injuries, frozen shoulder, nerve compression, and sports or work-related overuse injuries.
In most cases, a referral is not required to see a neck and shoulder specialist in Singapore. Patients may book a consultation directly, although referrals from a GP or physiotherapist can help provide prior medical context.
Diagnosis typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Depending on symptoms, imaging such as X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound scans may be recommended to identify joint, tendon, nerve, or spine-related causes.
No. Many neck and shoulder conditions respond well to conservative treatment such as physiotherapy, activity modification, and medication. A specialist will usually recommend surgery or injections only when non-surgical options are ineffective or symptoms are severe.
A neck and shoulder specialist is a medical doctor trained to diagnose underlying structural or degenerative conditions and advise on medical or surgical treatment when needed. Physiotherapists focus on rehabilitation, exercise therapy, and functional recovery under a guided treatment plan.
Recovery time varies depending on the condition, severity, and treatment approach. Some patients improve within weeks with conservative care, while chronic or degenerative conditions may require longer-term management and follow-up.
Although elbow pain may be localised to the joint itself, symptoms can sometimes be influenced by conditions affecting the spine or surrounding structures. Understanding related conditions helps ensure a thorough assessment and appropriate management plan.
Abnormal spinal curvature may alter overall body mechanics, leading to compensatory strain across the upper limbs and joints, including the elbow.
Low back pain may affect posture and movement efficiency, which can indirectly increase stress on the arms and elbows during daily or occupational activities.
Dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint can disrupt spinal alignment and load transfer, contributing to compensatory movement patterns that place additional strain on upper limb joints.
Auspicium Orthopaedic Centre is located at 3 Mount Elizabeth, #11-13, Singapore 228510.