- #11-13 Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre (Orchard)
- Mon Fri 9am — 6pm | Sat 9am — 12.30 pm
Low back pain, also known as lumbago, is a common and often frustrating experience that affects millions of people around the world. This is pain or discomfort felt in the lower back, specifically between the lower ribs and buttocks. This pain can range from a mild ache to a sharp and debilitating sensation, having a significant impact on daily activities and quality of life. Although low back pain can be alarming, it is important to understand that it is rarely a sign of a serious underlying condition and usually resolves with proper care and self-management.
The most important symptom of low back pain is localized pain in the lower back. This pain can vary in nature, including:
They have a clearly identifiable source, such as:
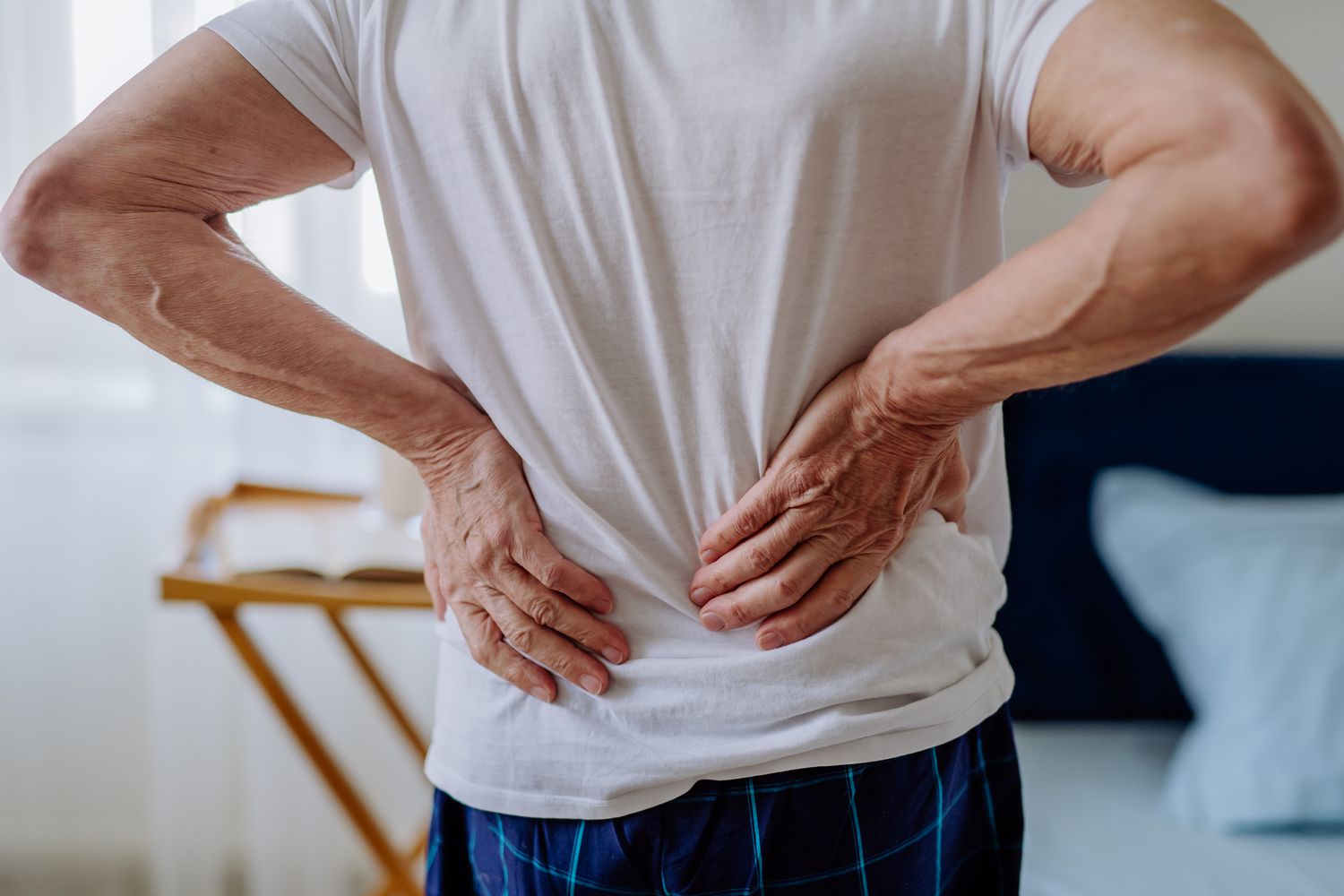
They have a clearly identifiable source, such as:
The good news is that most cases of lower back pain get better within a few weeks or months with conservative treatment. Treatment usually focuses on managing pain, reducing inflammation, and promoting healing.
Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee Pain
Ankle Pain
Foot Pain
Book a consultation with us for a more comprehensive diagnosis and a personalised treatment plan best suited to your needs.

Spine - Neck
Shoulder & Elbow
Spine — Back
Wrist & Hand
Knee
Ankle
Foot